Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL DROP TABLE statement to remove a table from the database.
Introduction to SQL DROP TABLE statement #
As the database evolves, you will need to delete obsolete tables from the database. To delete a table, you use the DROP TABLE statement.
Here’s the syntax for the DROP TABLE statement:
DROP TABLE table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)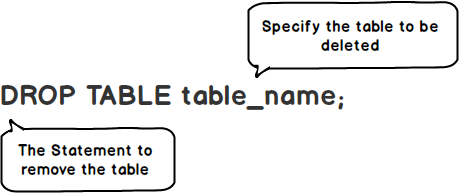
In this syntax, you specify the name of the table you want to drop after the DROP TABLE keywords.
The DROP TABLE statement removes both the data and structure of a table permanently.
If the table does not exist, the database system will issue an error.
To conditionally drop a table only if it exists, you can use the IF EXISTS option:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this case, the database system may issue a warning or notice if the table does not exist.
Note that to delete only data from a table, you use the DELETE or TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
SQL DROP TABLE statement example #
First, create a new table called emergency_contacts to store the emergency contacts of employees:
CREATE TABLE emergency_contacts (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
relationship VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
employee_id INT NOT NULL
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, use the DROP TABLE statement to drop the emergency_contacts table:
DROP TABLE emergency_contacts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary #
- Use SQL
DROP TABLEstatement to remove a table from the database.
Databases #
- PostgreSQL DROP TABLE Statement
- Oracle DROP TABLE Statement
- SQL Server DROP TABLE Statement
- MySQL DROP TABLE Statement
- SQLite DROP TABLE Statement
- Db2 DROP TABLE Statement
- MariaDB DROP TABLE Statement