Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL CONCAT function to concatenate two or more strings into a single string.
Introduction to SQL CONCAT function #
The SQL CONCAT function concatenates two or more strings into one string.
Here’s the syntax of the CONCAT function:
CONCAT(string1, string2,..);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To concatenate multiple strings, you pass them as a list of comma-separated arguments to the CONCAT function.
The CONCAT function returns a string which is the combination of the input strings. It returns NULL if one of the arguments is NULL.
You can use the IS NULL operator or COALESCE and NULLIF functions to handle NULL .
Most database systems support the CONCAT function with some differences among them.
For example, the CONCAT function in MySQL allows you to concatenate more than two strings, whereas the CONCAT function in Oracle Database concatenates exactly two strings.
Besides using the CONCAT function, you can use the concatenation operator, e.g., in Oracle and PostgreSQL, you can use the || operator to concatenate two or more strings. In Microsoft SQL Server, you use the + operator.
SQL CONCAT function examples #
The following statement uses the CONCAT function to concatenate two strings:
SELECT CONCAT('SQL CONCAT function', ' demo');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
concat
----------------------
SQL CONCAT function demo
(1 row)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement uses the CONCAT function to return the full name of the employees by concatenating the first name, space, and last name.
SELECT
CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) AS name
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
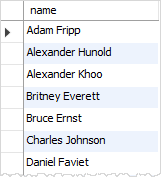
If you are using the Oracle Database, you have to apply the CONCAT function twice the achieve the same result:
SELECT
CONCAT(CONCAT(first_name, ' '), last_name) AS name
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The inner CONCAT function concatenates the first name with space and the outer CONCAT function concatenates the result of the inner CONCAT function with the last name.
Using the concatenation operator in Oracle (and also PostgreSQL) will be much cleaner.
SELECT
first_name || ' ' || last_name AS name
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In Microsoft SQL Server, you can use the + operator to concatenate strings like this:
SELECT
first_name + ' ' + last_name AS name
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you are using MySQL or PostgreSQL, you can use the CONCAT_WS function to concatenate strings with a separator.
CONCAT_WS(separator,string1,string2,...);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, you can use the CONCAT_WS function to construct the employee’s full names:
SELECT
CONCAT_WS(' ', first_name, last_name) AS name
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary #
- Use the SQL
CONCATfunction to concatenate two or more strings into a single string.
Databases #
- PostgreSQL CONCAT Function
- Oracle CONCAT Function
- MySQL CONCAT Function
- SQLite CONCAT Function
- Db2 CONCAT Function