The SQL COS function calculates the cosine of an input argument.
In math, given the ABC triangle, the cosine of an angle (A) is defined as the ratio between the length of the adjacent side (b) to the length of the hypotenuse (h) as follows:
cos A = b / hCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)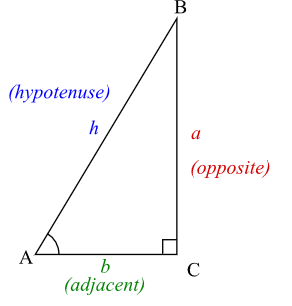
For the inverse of the COS function, see the ACOS function.
Syntax #
The following illustrates the syntax of the COS function:
COS(numeric_expression)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Argument #
The COS function accepts a numeric_expression that represents the angle in radians for which the cosine is calculated.
Return #
The COS function returns a floating-point number.
Examples #
The following example returns the cosines of 0, π, and π/3.
SELECT COS(0) cos_zero,
COS(PI()) cos_pi,
COS(PI()/3) cos_one_third_pi;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) cos_zero | cos_pi | cos_one_third_pi
----------+--------+------------------
1 | -1 | 0.5
(1 row)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that we use the PI function to get the π constant.
Most database systems support the COS function with the same behavior.