Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about SQL window functions that solve complex query challenges easily.
Introduction to SQL Window Functions #
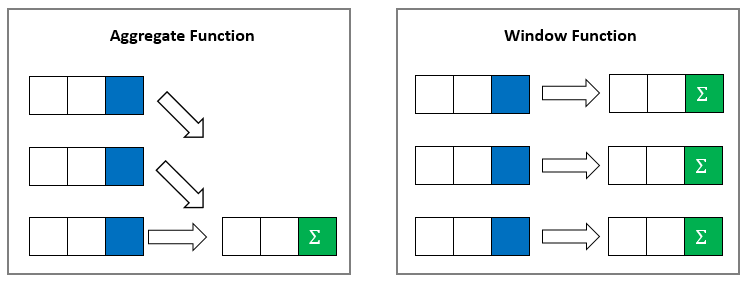
The aggregate functions perform calculations across rows and return a single output row.
The following query uses the SUM() aggregate function to calculate the total salary of all employees in the company:
SELECT
SUM(salary) total_salary
FROM
employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
total_salary
--------------
322400.00Code language: plaintext (plaintext)The output indicates that query group rows from the employees table into a single row.
Like an aggregate function, a window function operates on a set of rows. However, a window function does not group rows into a single row.
For example, the following query uses the SUM() function as a window function:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name,
salary,
SUM(salary) OVER () total_salary
FROM
employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It returns the salary of each individual employee along with the total salary of all employees:
first_name | last_name | salary | sum_salary
-------------+-------------+----------+------------
Steven | King | 24000.00 | 322400.00
Neena | Kochhar | 17000.00 | 322400.00
Lex | De Haan | 17000.00 | 322400.00
Alexander | Hunold | 9000.00 | 322400.00
Bruce | Ernst | 6000.00 | 322400.00
...In this example, the OVER() clause makes the SUM() function a window function.
The following picture illustrates the main difference between aggregate and window functions:
SQL window function syntax #
Here’s the basic syntax of a window function:
window_function_name ( expression ) OVER (
partition_clause
order_clause
frame_clause
)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)window_function_name
The window function name, such as ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), and SUM().
expression
The expression or column on which the window function operates.
OVER clause
The OVER clause defines a window or a partition. The OVER clause consists of three clauses:
- Partition By clause
- Order By clause
- Frame clause
The PARTITION BY clause divides the rows into partitions to which the window function applies. It has the following syntax:
PARTITION BY expr1, expr2, ...Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you don’t use the PARTITION BY clause, the window function treats the whole result set as a single partition.
The ORDER BY specifies the orders of rows in each partition:
ORDER BY
sort_expression [ASC | DESC] [NULL {FIRST| LAST}]
,...
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)A frame is the subset of the current partition. To define the frame, you use one of the following syntaxes:
{ RANGE | ROWS } frame_start
{ RANGE | ROWS } BETWEEN frame_start AND frame_end Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)where frame_start is one of the following options:
N PRECEDING
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
CURRENT ROWCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)and frame_end is one of the following options:
CURRENT ROW
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
N FOLLOWINGCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture illustrates a frame and its options:
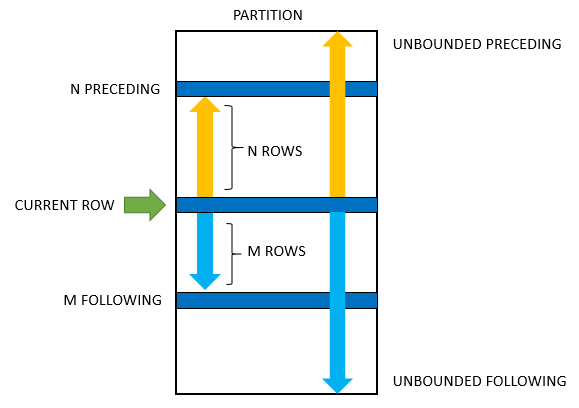
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING: the frame starts at the first row of the partition.N PRECEDING: the frame starts at the nth row before the current row.CURRENT ROW: means the current row that is being evaluated.UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING: the frame ends at the final row in the partition.N FOLLOWING: the frame ends at the Nh row after the current row.
The ROWS or RANGE specifies the type of relationship between the current row and frame rows.
-
ROWS: the offsets of the current row and frame rows are row numbers. -
RANGE: the offset of the current row and frame rows are row values.
SQL window function types #
There are three types of window functions including value window functions, aggregation window functions, and ranking window functions.
Value window functions #
Ranking window functions #
Aggregate window functions #
- AVG()
- COUNT()
- MAX()
- MIN()
- SUM()